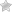Diagnosing diabetes enables the doctors and lab workers to detect and treat diabetes well before complications begin to occur [1]. It also helps to detect and cure prediabetes, which indicates greater risk of developing diabetes in future. Following tests are used nowadays to diagnose or detect diabetes:
- Oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)
- A1C or the hemoglobin A1c or the glycohemoglobin test
- Fasting blood sugar test

Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
The OGTT can be used to diagnose diabetes, prediabetes as well as gestational diabetes. OGTT measures blood sugar after 8 hours of fasting and 2 hours after the intake of a liquid containing 75 grams of glucose dissolved in water.
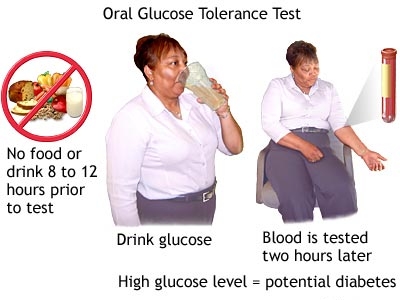
If the blood sugar level is 140 to 199 mg/dL, the person has prediabetes or impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). On confirmation by another test if,the glucose level is 200 mg/dL or above means that a person has diabetes.
A1C Test
The A1C test is used for detection of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes but does not diagnose type 1 or gestational diabetes. It is a blood test that determines the average blood glucose levels of a person over past 3 months but does not detect daily fluctuations. The A1C test can be performed at any time of the day and doesn’t require fasting which makes it convenient for patients.
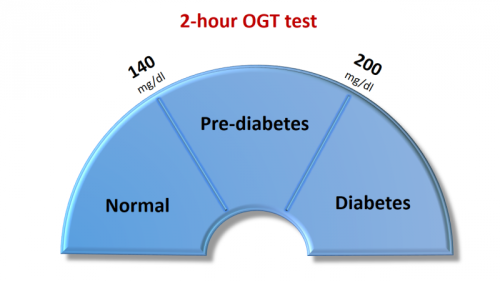
The A1C test result is obtained in percentage with 5.7% or lesser as normal value. A value of 5.7- 6.4% indicates prediabetes. A1C level above 6.0% is considered as very high risk of developing diabetes. A1C level of 6.5% or above indicates that a person has diabetes.
Fasting Plasma Glucose Test (FPG)
The Fasting blood glucose test detects both diabetes and prediabetes. It is the most common test used for the diagnosis of diabetes as it is more convenient than other tests like OGTT besides being less expensive. This test requires measurement of blood glucose in a person after fasting for a minimum of 8 hours. This test is performed most commonly in the morning.
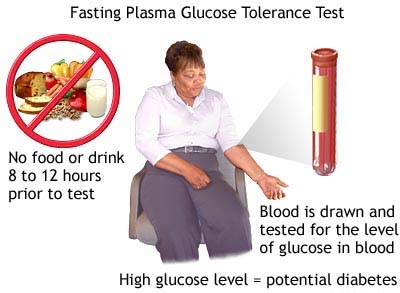
A fasting blood sugar level of 100 to 125 mg/dL is considered as prediabetes. The fasting blood sugar level of 126 mg/dL or more after repeating the test on another day confirms that a person is a victim of diabetes.
Treatment of Diabetes
Diabetes, even though a common disorder which has been fairly widespread throughout the world, is a chronic condition with no definitive cure. Even the non-chronic types of diabetes, namely prediabetes and Gestational Diabetes leave individuals at a risk of developing Type II Diabetes in the future. As such, the signs and symptoms of any type of diabetes must be taken seriously and the only possible methods of treatment include controlling these signs and symptoms and trying to make the bodily functions return to normal.
The main aim in treating diabetes is to lower the blood sugar level without causing hypoglycemia or a condition characterized by abnormally low levels of blood sugar. Whatever the type of diabetes may be and whatever treatment plan is being adhered to, care must be taken that the blood sugar levels are monitored on a frequent and consistent basis. Monitoring is the first step in determining the severity of diabetes and it is then followed up with deciding on the appropriate measures to be taken in order to control the condition.
Prediabetes is the stage where one can control the blood sugar level from rising and prevent diabetes from occurring [2]. This can be treated with adequate amounts of exercise followed in conjunction with a diabetic diet. In some rare cases, oral medication may also be prescribed, especially if there has been a history of preeclampsia or Gestational Diabetes in the past.
Type I Diabetes is treated with exercise, diabetic diet and external insulin administration. Insulin may be injected intravenously or an insulin pump may be used to administer the dose. Active medical and scientific research is being done in order to come up with newer and more convenient methods of externally administering insulin to diabetics. Insulin cannot be administered orally as the enzymes present in the human stomach interfere with the functioning of insulin.
There are some extremely rare cases in which a transplantation of the pancreas is used in order to treat Type I Diabetes. This is only carried out if some other organ of the body has also failed and requires transplantation such as the kidneys. However, this process may yield dangerous effects on the body and also results in higher chances of infections to internal organs.
Type II Diabetes is first treated with exercise, weight reduction and a diabetic diet. In case these measures prove to fail in controlling the disease, oral hypoglycemic drugs such as metformin, prandin, glimepiride and pioglitazone are used. If oral medications are still insufficient, treatment with insulin or insulin analogues like insulin Lispro, insulin Glargin and insulin Aspart are considered useful.
Bariatic surgery is a lesser used method to treat Type II Diabetes. People who have a BMI greater than 35 may see improvements in conditions by undergoing this type of surgery.
Gestational Diabetes can be treated by exercise and diet modification. Only 15% of women with gestational diabetes need medications like oral hypoglycemics or sometimes insulin analogues. However, any female who has experienced an episode of Gestational Diabetes stands a risk of developing the condition again in subsequent pregnancies and may also develop prediabetes and Type II Diabetes in the future. As such, care and treatment procedures will need to be continued throughout the life of the diabetic.
Weight reduction and exercise are important treatments for diabetes. Weight reduction and exercise increase the body’s sensitivity to insulin, thus helping to control blood sugar elevations. A diabetic diet is also an important measure to prevent as well as control diabetes. It is recommended that diabetics have more of fruits, vegetables and whole grains in the diet. Fatty foods and sugary foods should be avoided as far as possible. A diabetic diet often involves a calorie count which is supposed to be strictly adhered to.
Signs of Danger in Diabetics
While there may be many methods to help control the symptoms of diabetes, care must be taken not to lower the blood sugar levels abnormally and also to prevent other potential hazards [3]. Some of the signs of danger that must be taken heed of at the earliest include:
- An increased presence of ketones in the urine. Ketones are toxic produces of the body when it breaks down fat for energy rather than using glucose. This condition is known as Diabetic Ketoacidosis and is accompanied with an extreme loss of appetite, a general feeling of weakness and fatigue, nausea and vomiting, stomach pains and also fever. This condition is more frequently associated with Type I Diabetes.
- Hypoglycemia or a low blood sugar level is also a complication associated with improper treatment of diabetes. This is likely to happen if, during the course of treatment, a meal is skipped or higher than normal physical activity is undergone. This condition is characterized by a feeling of dizziness, sweating, jitters, extreme hunger, blurring of the vision and palpitation of the heart, confusion, faintness and even seizures. The condition can be quickly remedied by having glucose tablets or a fruit juice.
- Extremely high blood sugar levels can lead to a condition known as hyperglycemia and this can adversely affect the condition of a diabetic. The signs and symptoms of the condition include the frequent need to urinate, dehydration and dryness, fatigue and blurred vision and the condition requires adjustments made to both the dietary plan as well as the medications used for treating diabetes.
- A life threatening complication involves an extremely high blood sugar level, typically around 600mg/dL. This condition is extremely serious and is known as hyperglycemic hyperosmolar non-ketotic syndrome and is characterized by the sugar present in the blood to turn thick and syrupy. It causes hallucinations, loss of vision, confusion and seizures and can also lead to death. This condition is more commonly associated with Type II Diabetes.
If any complications and symptoms are experienced by individuals, immediate medical attention needs to be provided at the earliest. These conditions can potentially be life-threatening and must be controlled at the earliest before too much damage has been inducted.
Alternative Remedies for Diabetes
There are some alternative medication procedures and therapies which may prove to help in controlling the symptoms of diabetes. While there are some such therapies, none of them are clinically proven and there is no established or agreed benefit upon resorting to these therapies. If individuals are keen on seeking alternative medications and therapies, they should do so only after proper medical consultation.
Diabetes does not have any treatment and it is a potentially life-threatening condition. Diabetics must take care to adhere to a strict treatment plan which is recommended and also approved.
Home Remedies and Lifestyle Tips for Diabetes
Since diabetes does not have a definitive cure, patients must learn to cope up with the disease and bring about healthy changes to diet and lifestyle in order to lead a close to normal life. This means that the diabetic individual will require to actively take measures through all aspects of life and to also seek proper medical treatment.
A strong mental commitment to fight the disease is the first and foremost step that must be taken in order to beat the symptoms. Diabetic individuals are urged to find out as much about the disease as possible, its methods of containment and also the various complications that may be associated with diabetes.
Any excess weight should be shed off and regular physical activity is highly recommended to diabetics. This highly increases the sensitivity of the body to insulin and also makes sure that the cells of the body can absorb sugar more effectively. Regular exercise should always be combined with a diabetic diet after taking consultation from healthcare providers or dieticians.
Diabetics are also advised to always carry along with them a tag which mentions that they are diabetics who may require assistance in cases of emergencies [4]. A glucagon kit should also be carried along at all times and the close friends and family of a diabetic should learn how to properly administer insulin in cases of emergencies.
Medical checkups, which involve not just the monitoring of the blood sugar levels, but also the checking of sensitive regions for any potential damage caused to the blood vessels and the nerve tissues, should be carried out on a frequent basis. Eye checkups are also recommended to be had frequently.
Vaccinations against different types of infections should always be taken on time. Diabetics are more prone to develop infections and the healing process is also slow in diabetics. It is a must that they ensure to keep themselves vaccinated and always up to date.
Blood pressure levels and cholesterol levels must always be kept in check. In some cases, medications may also be used to keep these in check.
Special attention should be given to the gums, the teeth, the feet and also the genital areas when diagnosed with diabetes. These regions of the body are much more prone to infections than other parts and medical attention needs to be provided at the earliest in case of any problems.

Alcohol should always be had after careful consideration. Not only may the alcohol and the associated mixing drinks upset the diabetic diet, but excess of alcohol can prove to cause complications in diabetics. The recommended amount of alcohol to be consumed is not more than one drink for a woman and not more than two for a man.
In case a person diagnosed with diabetes mellitus is a smoker, cessation of smoking must be done at the earliest [5]. Use of tobacco greatly increases the risks of complications and may also lead to the development of cardiovascular diseases in diabetics. Cessation of smoking is not easy and often, special alternatives and other nicotine products are the starting point to quitting smoking.
Diabetics may be prone to be hypertensive and stressful. This stress will always need to be effectively managed as there is already enough abnormal pressure on the delicate blood vessels and the nerves of a diabetic. Plenty of sleep, meditation and relaxation are recommended to diabetics in order to keep stress levels in check.
References
[1] Changing the Way Diabetes is Treated With Information and Resources, James R. Gavin III, MD, PhD; 24 no. 1 14-16 – January 2006 – DOI: 10.2337/diaclin.24.1.14Clinical Diabetes, http://clinical.diabetesjournals.org/content/24/1/14.short
[2] Continuous glucose monitoring and intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes, Tamborlane WV,Beck RW, Bode BW, Buckingham B, Chase HP, Clemons R, Fiallo-Scharer R, Fox LA, Gilliam LK, Hirsch IB, Huang ES, Kollman C, Kowalski AJ, Laffel L, Lawrence JM, Lee J, Mauras N, O’Grady M, Ruedy KJ, Tansey M,Tsalikian E, Weinzimer S, Wilson DM, Wolpert H, Wysocki T, Xing D,; 359(14):1464-1476 – September, 2008 – DOI: 1056/NEJMoa0805017, http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/18779236,,
[3] A Randomized Trial of Therapies for Type 2 Diabetes and Coronary Artery Disease, The BARI 2D Study Group,; 360(24): 2503–2515 – Jun 7, 2009 – DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0805796, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2863990/
[4] Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategies, Jay S. Skyler,; 47 (17), pp 4113–4117 – July 20, 2004 – DOI: 10.1021/jm0306273, http://pubs.acs.org/doi/abs/10.1021/jm0306273?journalCode=jmcmar
[5] The Burden of Treatment Failure in Type 2 Diabetes, Jonathan B. Brown, PHD, MPP1, Gregory A. Nichols, PHD1and Andrew Perry, MA HONS, MSC2.; 27no. 7 1535-1540 – July 2004 – DOI: 10.2337/diacare.27.7.1535, http://care.diabetesjournals.org/content/27/7/1535.short